Etherscan Basics
7 minutes
Feb 1st, 2023 - 11:13 am
What is Etherscan?
Etherscan is a popular blockchain explorer that allows users to view and search the Ethereum blockchain. It provides a wide range of information and tools for users, including the ability to view transactions, lookup addresses, and interact with smart contracts. In this article we will cover:
- Viewing transactions
- Looking up addresses
- Interacting with smart contracts
- Tracking tokens
- So… Is This Contract Legit?
- Analyzing network statistics (e.g. current gas price)
Viewing Transactions
A common scenario is wanting to see the status of a pending transaction to check if it has been included in a block, or whether you need to speed it up. Here’s how to check:
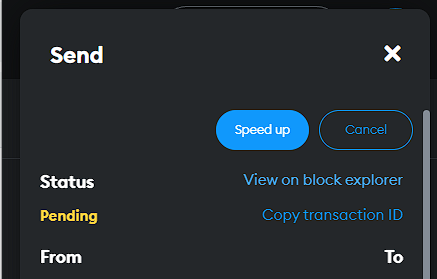
From MetaMask or your wallet of choice, click the pending transaction and copy its transaction hash (MetaMask calls this the “transaction ID”). Then navigate to Etherscan.io, input the transaction hash into the search bar and hit enter. (Alternatively in MetaMask, you can simply hit “view on block explorer”). You can now see the transaction. Here’s what the fields mean:
| Field | Definition |
| Status | Status denotes the status of the transaction. It will always be one of the following:
|
| Transaction Hash | This is the unique hex string that identifies the transaction. |
| Block Number | This is the block number that the transaction was included in. |
| Date/Time | This is the date and time that the transaction was processed by the Ethereum network (or in the case of a pending transaction, when the transaction was last seen in the mempool). |
| To/From Addresses | These are the address sending the transaction (from) and the receiving address/contract being called (to). |
| Value | This is the amount of Ether transferred in the transaction. |
| Txn Fee | This is the amount of Ether that was spent on gas to process the transaction. |
| Input Data | This is the data that was included in the transaction (for sending to a contract, this field instructs which function you are calling and the arguments of said function). |

There is a handy gas tracker here which can show us the estimated time until the transaction is included in a block: here we can see it is over an hour, and so if we want to have it confirmed quicker we should speed it up (Metamask How To: Speed up a transaction)!
Looking Up Addresses
You can also use Etherscan to view the balance and transaction history of any Ethereum address. There are two types of Ethereum addresses, Contract (NFTs, tokens, multisig vaults like Gnosis, etc.) and EOA (Externally Owned Address, otherwise known as wallet addresses), and they each display in Etherscan a bit differently. To search, simply enter the address (or ENS name) into the search bar on the homepage, and you will be taken to a page displaying the address details, including the balance, transaction history, and any smart contracts associated with the address.

On the address page you can view the following info:
- The address: This is the unique string of characters that represents the Ethereum address (42 characters long, beginning with “0x”).
- The balance: This is the current balance of Ether for the address. You can also view ERC20/721/1155 tokens owned by the address.
- The transaction history: This is a list of all confirmed Ethereum transactions to and from this address.
- The token tracker: If the address is a contract address for a token, you can track the token transactions, holders, and their balances.
- The contract: If the address is a smart contract address, you can see the contract's details, including the contract code, transaction history, and any emitted events.
- The internal transactions: You can see the internal transactions to this address (and for smart contracts, internal transactions from the address also). Internal transactions are explained in more detail in our 102 course, but internal transactions are simply transactions that occur between smart contracts. This can also include transactions from a smart contract to an external address when sending ETH to a user. This is useful to understand and explore, as you may find more transactions surfacing here on your address than you might think! If you've signed up for our 102 class, we bulk send ETH on the Goerli test network, and you won't see it in your transactions tab, only your Internal Txns tab!
You can also filter the transactions by date, block number, address to/from, and method using the filter buttons on the columns. The menu above “txn fee” allows you to filter by failed/pending transactions as well as incoming/outgoing transactions.
Interacting With Smart Contracts
Smart contracts can be viewed the same way as above, but have some additional features compared to regular EOAs (externally owned addresses):
- The contract name: If the contract is verified, you can see the contract's name.
- The contract code: This is the source code of the smart contract, which you can view and analyse.
- The contract creator: This is the Ethereum address that deployed the contract to the blockchain.
- The transaction history: This is a list of all transactions that have been processed by the Ethereum network involving this contract.
- The events: This is a list of events emitted by the smart contract, including the event signature, data and topics.
- The read/write tabs: This allows you to call read/write functions of the contract: you could use this to stake Apecoin directly from Etherscan, or to increment your seaport nonce as in this article.
For a tutorial of how to interact with a contract on Etherscan, see the embed below:
Tracking Tokens
For tokens, we can view a page which gives details like token transfers, social media accounts, holders and more.
Navigate to the token tracker page by entering the token’s contract address in the Etherscan search bar, same as for looking up addresses. Then click the link under “token tracker” if you are brought to the address rather than the token page.


We can now view the:
- Token Name: This is the name of the token, as specified in the smart contract.
- Token symbol: This is the symbol of the token, as specified in the smart contract.
- Total supply: This is the total number of tokens that were created by the smart contract.
- Holders: This is a list of addresses that hold the token and the amount of tokens they hold.
- Transfer history: This is a list of all transfers of the token.
For NFTs, the “NFT Trades” will show a list of sales on supported marketplaces. For ERC20 tokens, the “DEX Trades” tab will show recent buys/sells on supported DEXs (Uniswap etc). ERC20s also have a chart tab which will allow you to see the buys/sells of specific DEXs on a tradingview widget which can let you analyse price action.
Is This Contract Legit?
So now that you know a lot of the basics, one of the best use cases from a security perspective is to vet what you interact with. Whenever you are making a transaction, you're likely interacting with a contract. But how do you know if that contract is legit, or the correct contract? Well, once you determine its legitimacy, you shouldn't have to keep doing it with that same contract! Something that we stress in our 101 course is to utilize Metamask Bookmarks for contracts for two main reasons:
- If you go to a website you normally interact with and make a familiar contract interaction, you would expect it to show up like in the figure below.
- If you are going to a website you don't normally go to, say to mint an NFT, you'd be rather surprised if one of your high value NFT or token contracts popped up instead of a random 0x____ address, right?

But before we add something to our bookmarks, we should first examine and scrutinize it on Etherscan (and potentially other places as well as part of your DYOR routine), here are some things that etherscan vets and surfaces to its users that add to my confidence level in that I am actually interacting with a real and reputable contract:
- Blue Verification Checkmark: This is different from the Contract Verification Green check, which simply confirms that the code uploaded to Etherscan matches the bytecode deployed to the Ethereum Network. The Blue Verification checkmark measures how well known a project is, how frequently the project's socials, contracts, and ecosystem is, as well as a number of other binary factors (including the aforementioned contract code verification “green check”).
- Token Reputation: Although a number of factors go in to this as well, Etherscan maintains that it is not an endorsement, but rather another set of criteria users can use to determine its legitimacy. It takes factors such as ICO age, if the project is traded on a KYC/AML enforced exchange, and more.
- Public Name Tags: Public name tags and labels are put on a project Etherscan page by the Etherscan team in order to help users make a more informed decision about it. Generally these are letting a person know about what a project is, but can sometimes also be used to label hacker/exploiter addresses as well as notable figures.
Note: It is important to know that token names in Etherscan are NOT verified just because they are listed on Etherscan. Anyone can deploy a token name and have it be anything they want.
Bonus: Analyzing Network Statistics
Etherscan also provides network-wide statistics, such as the total number of transactions, the total number of addresses, and the total amount of Ether in circulation, viewable on the Etherscan homepage. Some of these include:
- Total number of transactions: This is the total number of transactions that have been processed by the Ethereum network.
- Total number of addresses: This is the total number of unique addresses that have been used on the Ethereum network.
- Total amount of Ether in circulation: This is the total amount of Ether that exists on the Ethereum network, including both in circulation and locked in smart contracts.
- Active nodes: This is the number of nodes currently connected to the network.
- Network's transactions per day: This is the number of transactions processed on the network in a 24-hour period.

However, there is one very important statistic you should be familiar with, gas price. You can think of the current gas price as the current demand for blockspace i.e. the price people are willing to pay to have their transactions processed. Looking at our pending transaction at the start of the article, we can figure out exactly how much we need to pay to get our transaction processed in a timely manner by visiting etherscan.io/gastracker, where gas prices and their current times to confirm are listed. Another handy site to dive into gas usage on the network is UltraSound Money. Use this site to see anything from which contracts are using the most gas, the ETH inflation/deflation rate statistics, ETH staking stats, and more!
Wrapping up
Hopefully this gives you an insight into the different features Etherscan offers, and how they might be utilised. If you want to learn more about it, we do a dive and some hands-on exercises in the Boring Security 102 class, which will net you this NFT as well! Etherscan also has a pretty extensive knowledge base, and many answers to your questions can be found simply by typing it in the search bar found on the site!
Disclaimer: Though there has been little reason to doubt what etherscan shows in the past, Etherscan is a 3rd party service, and its employees are not immune to social engineering or potential bribery, so interact with caution. You can always reference information with other blockchain explorers (e.g. Blockchair) to get a second source just in case or if etherscan is down!
Have any questions or want to learn more about web3 security and stay up to date on the most current security information, scams, and tactics? Join us in our discord at https://discord.gg/boringsecurity .

